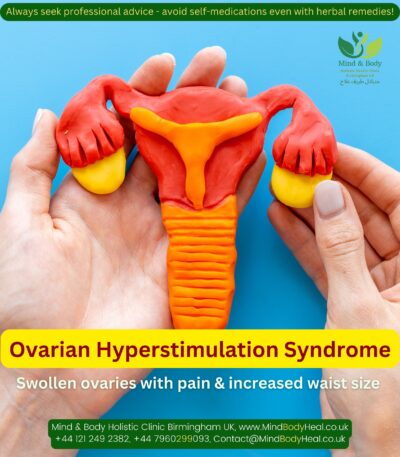
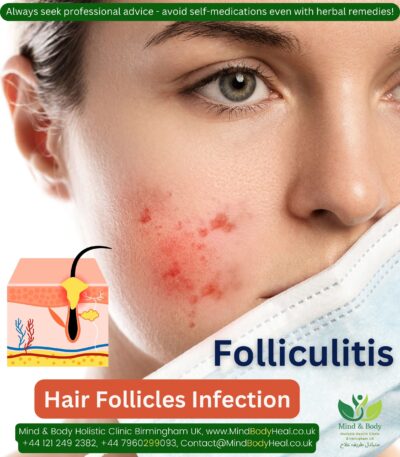
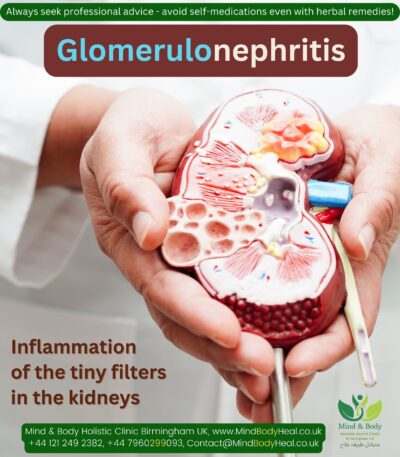
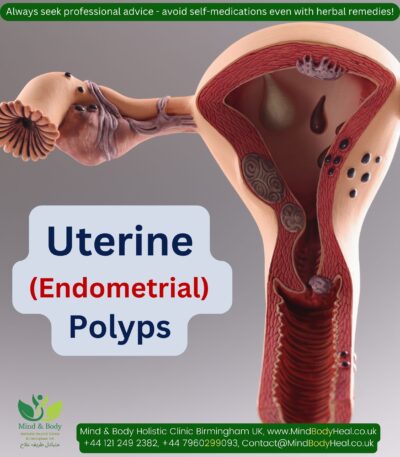
Infertility in women.
Infertility is not being able to get pregnant despite having frequent, unprotected intercourse for at least a year with no success for women under 35 OR 6 months if the woman is over the age of 35!
Infertility is a relative state of failure to conceive whereas sterility is the absolute state of inability to conceive.
- Infertility cases are increasing all over the world.
- Around 10% – 15% couples are facing infertility problems.
- Available data suggests that around 48 million couples and 186 million individuals have infertility globally.
- The condition affects both men and women equally!
There are 2 types of Infertility
- Primary infertility refers to women who NEVER conceived or become pregnant.
- Secondary infertility refers to those who have been able to get pregnant at least once in the past but are unable now for certain reasons.
Although the ability to conceive starts to fall around the the age of 35 years.
Yet worldwide available data confirms that many women have given births, in their 60’s & even 70’s.
Female infertility causes can be difficult to diagnose as the cause is either unknown or a combination of male and female factors.
A thorough checkup of both partners is necessary to know the possible causative factors and get treatment accordingly.
Contact our clinic in Birmingham UK, for your detailed assessment for you to take treatment as per your specific causes to increase chances of conception!
Symptoms of a Female Infertility
- The main symptom of infertility is the inability to get pregnant or to conceive.
- A menstrual cycle that’s too long (35 days or more), too short (less than 21 days), irregular or absent can mean that you’re not ovulating.
There are roughly over 50 Possible Causes of Female infertility
- It you tell us yours – we will help and plan your treatment protocol accordingly!
- There are many holistic treatments available, depending on the infertility specific cause.
Possible causes and factors of female infertility.
The causes in men are a low sperm count, malformed sperms, testicular maldevelopment while in women it could be due to lack of ovulation, uterine and ovarian malformations or infections of the genital tract.
Some prominent factors are listed below:
- Endometriosis that accounts for up to 50% of female infertility: When cells that normally occur within the lining of the uterus start growing elsewhere in the body.
Endometriosis can also disrupt implantation of the fertilized egg. The condition also seems to affect fertility in less-direct ways, such as damage to the sperm or egg.
- Irregular periods or an absent menstrual cycle can be a sign of lack of ovulation, which can be associated with infertility – and is the 2nd leading cause of about 30% cases.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common factors of female infertility, that causes a hormone imbalance, which affects ovulation.
PCOS is associated with insulin resistance and obesity, abnormal hair growth on the face or body, and acne.
- Primary ovarian insufficiency, also called premature ovarian failure or syndrome, is usually caused by an autoimmune response or by premature loss of eggs from your ovary, possibly as a result of genetics or chemotherapy. Where the ovary no longer produces eggs, and it lowers oestrogen production in women under age 40.
- Structural abnormality or weakness in the female reproductive organs i.e., in uterus / cervix etc
- Submucosal fibroids: Benign or non-cancerous tumors occur in the muscular wall of the uterus. They can interfere with implantation or block the fallopian tube, preventing sperm from fertilizing the egg. Large submucosal uterine fibroids may make the uterus’ cavity bigger, increasing the distance the sperm has to travel.
- Hormonal abnormalities – low progesterone levels or too much prolactin
- Discharge of mucus after coitus or semen leakage after sexual intercourse.
- Chronic, persistent leucorrhea – thrush / candida or yeast infections (white discharge)
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Gonorrhoea or Chlamydia etc., can damage the fallopian tubes in women and cause inflammation in a man’s scrotum.
- Tubal infertility – damaged or blocked fallopian tubes keep sperm from getting to the egg or block the passage of the fertilized egg into the uterus.
- Sexual history. Having unprotected sex with multiple partners increases your risk of a sexually transmitted infection that may cause fertility problems later.
- Vaginismus – constricted, sensitive vagina – painful coition may lead to fear of physical contact
- Past Pelvic surgeries can sometimes cause scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes. Cervical surgery can sometimes cause shortening of the cervix.
- Previous sterilization treatment: In women who have chosen to have their fallopian tubes blocked, the process can be reversed, but the chances of becoming fertile again are not high.
- Endocrine dysfunction from hypothalamus to pituitary to thyroid and to ovary glands.
- Hypothalamic dysfunction. Two hormones produced by the pituitary gland are responsible for stimulating ovulation each month — follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Excess physical or emotional stress, a very high or very low body weight, or a recent substantial weight gain or loss can disrupt production of these hormones and affect ovulation. Irregular or absent periods are its most common signs.
- Too much prolactin. The pituitary gland can cause excess production of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia), which reduces oestrogen production and can cause infertility.
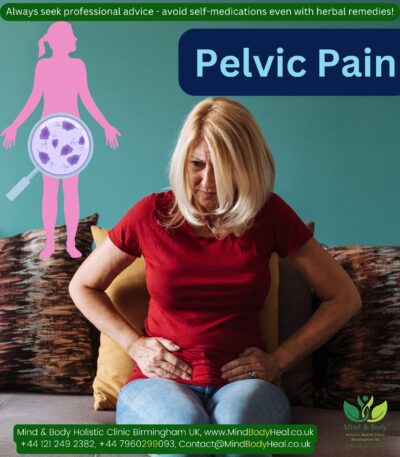
- Pelvic inflammatory disease, an infection or inflammation of the uterus and fallopian tubes due to chlamydia, gonorrhoea or other sexually transmitted infections.
- Pelvic T.B or pelvic adhesions due to infection or following surgery.
- Benign polyps or tumors (fibroids or myomas) are common in the uterus. Some can block fallopian tubes or interfere with implantation, affecting fertility.
- Problems with the uterus present since birth, such as an unusually shaped, bulky or tilted uterus.
- Cervical stenosis, a narrowing of the cervix, can be caused by an inherited malformation or damage to the cervix.
- Sometimes the cervix can’t produce the best type of mucus to allow the sperm to travel through the cervix into the uterus.
- Poor nutrition or diet: A lack of folic acid, iron, zinc, and vitamin B 12 can affect fertility. Women who are at risk, including those on a vegan diet, should ask their doctor about supplements.
- Eating disorders e.g., anorexia nervosa and bulimia etc., can lead to serious weight loss, fertility problems may arise.
- Constant exposure to chemicals, pesticides, herbicides, household detergents, metals, such as lead, and solvents have been linked to fertility problems too, as they may interfere with hormonal system.
- Smoking significantly increases the risk of infertility in both men and women, and it may undermine the effects of fertility treatment. Smoking during pregnancy increases the chance of pregnancy loss. Passive smoking has also been linked to lower fertility.
- Being obese or overweight: This can increase the risk of infertility in women as well as men.
- History of Diabetes
- Radiations or cancer treatments
- Celiac / Kidney disease.
- Exercise: Both too much and too little exercise can lead to fertility problems.
- History of ectopic (tubal) pregnancy.
- Atrophy of glands like breasts and ovaries (shrinkage or wasting underdeveloped).
- Intake of high-fat processed meats / junk foods can increase inflammation levels and may contain additives.
- Grains – may increase cortisol and estrogen, leading to infertility issues.
- Refined sugar reduces immune function and may cause nutrient depletion. High intake of refined sugar also contributes to obesity, which is a big risk factor for infertility.
- Use of certain medicines and drugs: The long-term use of NSAIDs, e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin, antipsychotics, chemotherapy medications, use of anabolic steroids, spironolactone – a type of medicine used to treat fluid retention (oedema) etc.
- Illegal drugs, such as marijuana and cocaine, can seriously affect fertility and make ovulation more difficult.
- Alcohol – increases inflammation and reduces immune function. For women, it is associated with an increased risk of ovulation disorders. For men, it lowers testosterone levels, causes erectile dysfunction and decreases sperm production.
- Caffeine – can cause hormonal imbalances, dehydration and lead to mineral deficiencies. High consumption has been shown to interfere with fertility. Lowering your caffeine or giving it up entirely is a smart idea when you’re trying to get pregnant, especially if you’re having trouble.
- Chromosomic defects
- Use of synthetic lubricants during sexual activity.
- Thyroid disorders.
- Poor female ovum (weak eggs condition)
- Sickle cell Anemia
- Sexual contact during least fertile days / time & opting least effective positions for conception.
- Emotional factors: Mental stress may affect female ovulation, male sperm production and can lead to reduced sexual activity.
Factors like:
Psychological trauma, sleep disorders Chronic depression, anxiety, fear of coition, partner’s negligence towards each other can lead to absent / decreased intimate desire (libido) – result in reduced sexual activity too.
Unexplained frustrating infertility – In some cases, the cause of infertility is never found. A combination of several minor factors in both partners could cause unexplained fertility problems.
When is a woman least fertile?
Calculate your fertile window.
- It’s good to know the best time to have sex.
- Women are typically at their least fertile right before menstruation, during menstruation and just after menstruation.
What is the most fertile window?
Days 8-19 are considered the most fertile; usually, 12 to 14 days before your next period starts.
Yet, it’s possible to get pregnant at any time of the month.
Possible Signs of ovulation to notice during fertile window – one the ovulation day;
- Your cervix may soften & open-up and its mucus becomes clearer and thinner with a more slippery consistency like egg whites.
- Breasts feel tender and very sensitive.
- Mild aches or pain is felt in the lower abdomen.
- Sex drive (libido) may increase.
- You may notice some light spotting.
- Vulva or vagina may appear swollen.
- Nausea, bloating / change in smell (may increase)
How to increase your chances of conception?
- Start tracking your menstrual cycle
- Identify your fertile window and start tracking ovulation.
- Make sure to have unprotected sex more frequently during the fertile window.
- Morning may be the best time to have sex for conception, at least as far as sperm are concerned.
- The right sexual position is also equally important.
- Opt for positions that allow for deeper penetration, e.g., where the male partner is on top, may help deposit sperm closer to the uterus.
- Make sure you’re using a fertility-friendly lubricant, if needed.
- Lay down & relax for a few minutes after sex.
TEMPERATURE METHOD
Your body temperature falls slightly, then rises again during your fertile days.
Take your temperature every morning before getting out of bed and chart it.
When your temperature rises by 0.3 -0.6 *C, it means that ovulation has occurred, and this period is your fertile period (In fact the fertile period starts 3/4 days prior to the temperature change).
DO’S & DONT’S
- The couples’ care, love, respect and understanding for each other are important factors for the child development.
- Always be honest with your partner and re-establish intimacy with your partner if affected.
- Do not blame your spouse for infertility as both partners are equally responsible.
- Relax before intercourse, do not get stressed and try to enjoy the experience – Active foreplay will make the act more rewarding.
- Get More Sleep – important for improving fertility. If you don’t get enough sleep, your cycle as well as ovulation can get disturbed.
- Exercise to Balance Hormones – exercise improves the mood, sleep and an increase in libido, promotes a healthy waistline and help your chances of conceiving.
- Stress has a direct impact on a woman’s risk for infertility.
- If you’re stressed out, your cortisol levels are elevated, that leads to not only infertility, but all sorts of other physical and mental problems as well.
- Find healthy ways to deal with your emotions / stress.
- Speak with a trusted health provider or counselor.
- Explore your options.
- Join an infertility support group.
- A diet with zinc and Vitamin C helps increase sperm count in men.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking, esp. before intercourse.
- If the semen flows out after intercourse, then the female should keep a pillow under the lower back in order to tilt the pelvis and should remain in this position for an hour.
- Stop all contraceptive methods at least two months before you plan a child.
FREE Shipping included – Usually dispatched within 1 – 2 working days!
Are you concerned about your health or managing a recurring or chronic condition?
Our website provides informed guidance and initial supportive care for individuals who are finding it difficult to access their doctors or who have not experienced desired improvement with conventional options.
We help individuals explore a range of natural and holistic healing approaches to encourage balance and long-term wellness that may complement your healing journey.
We offer a ready-to-use complementary remedies kit designed to ease discomfort and support well-being, with clear instructions for each item.
The kit includes a personalised selection of remedies based on your signs, symptoms, and likely causative factors.
It may combine homeopathic medicines, herbal or daily supplements, a tailored diet plan, lifestyle guidance, practical tips, and topical applications where needed. It’s suitable if you value the healing potential of natural, holistic remedies.
Complementary remedies work best alongside standard medical treatments and can usually be taken safely with your regular medications.
Our homeopathic remedies follow Dr. Hahnemann’s traditional dilution and succussion methods and are prepared by a qualified naturopathic practitioner, supported by research, clinical experience, and observed outcomes in similar cases. Treatment duration can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on severity and chronicity. Outcomes vary with individual factors and case complexity.
If you prefer lactose pills instead of sucrose globules, let us know. Please also provide the patient’s age so we can supply appropriately sized pills. You can simply send this via WhatsApp at 07960 299 093.
These remedies may contain trace amounts of natural plant, mineral, or animal substances, preserved in medical-grade alcohol. Inform us of any allergies or dietary restrictions before purchase.
You may contact us before starting or book a detailed consultation (in person or via teleconsultation) with one of our experienced naturopath for your detailed assessment or personalized guidance.
Natural remedies can affect the body and may not suit everyone. At the start of treatment, some patients—especially with mental health or skin issues—may experience a temporary increase in symptoms. This may represent medicinal aggravation, indicating the body is responding, though symptoms may not be connected and simply coincidental. If they persist, contact us for support.
Why some patients choose natural, complementary or holistic remedies:
• Symptomatic relief and improved well-being
• Gentle options with fewer side effects
• Whole-person focus, addressing physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors
• Root-cause and preventive emphasis
• Encouragement of active self-care
• Support alongside conventional treatment
• Personalised and accessible care
Precautions:
• Inform your healthcare provider about any complementary therapies
• Some herbs or supplements may interact with conventional medications
• Do not replace conventional treatment for serious, chronic, or terminal conditions
These complementary remedy kits are provided for your own discretion and personal responsibility. Use them mindfully and avoid self-medicating in sensitive situations.
If you are looking for a specific remedy / kit not listed on our site or a customized formulation, contact us—our range is extensive and can be tailored to your physical and mental symptoms and causative factors.
Disclaimer:
Natural remedies—including homeopathic remedies, herbal supplements, and aromatherapy products—are generally safe for most people, including children and older adults. Still, consult your GP or healthcare provider before use, especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or managing chronic or serious conditions.
- Our remedies support general wellness and are not a substitute for medical advice.
- Review product details and make informed decisions before purchasing, particularly for ongoing or serious concerns.
- We provide general guidance only; detailed personalised consultations are not available through this platform.
- These remedies are intended for individuals able to follow instructions independently.
- Our support focuses on product use and general information; repeated or highly detailed personal queries may not receive individual responses.
- If you need frequent reassurance or highly tailored advice, please consult a qualified naturopath or healthcare provider before purchasing.
Due to strict UK regulations on the sale of medicinal products, we cannot give specific advice, without a face-to-face consultation.