Thrombophlebitis – Thrombosis – Blood Clots:
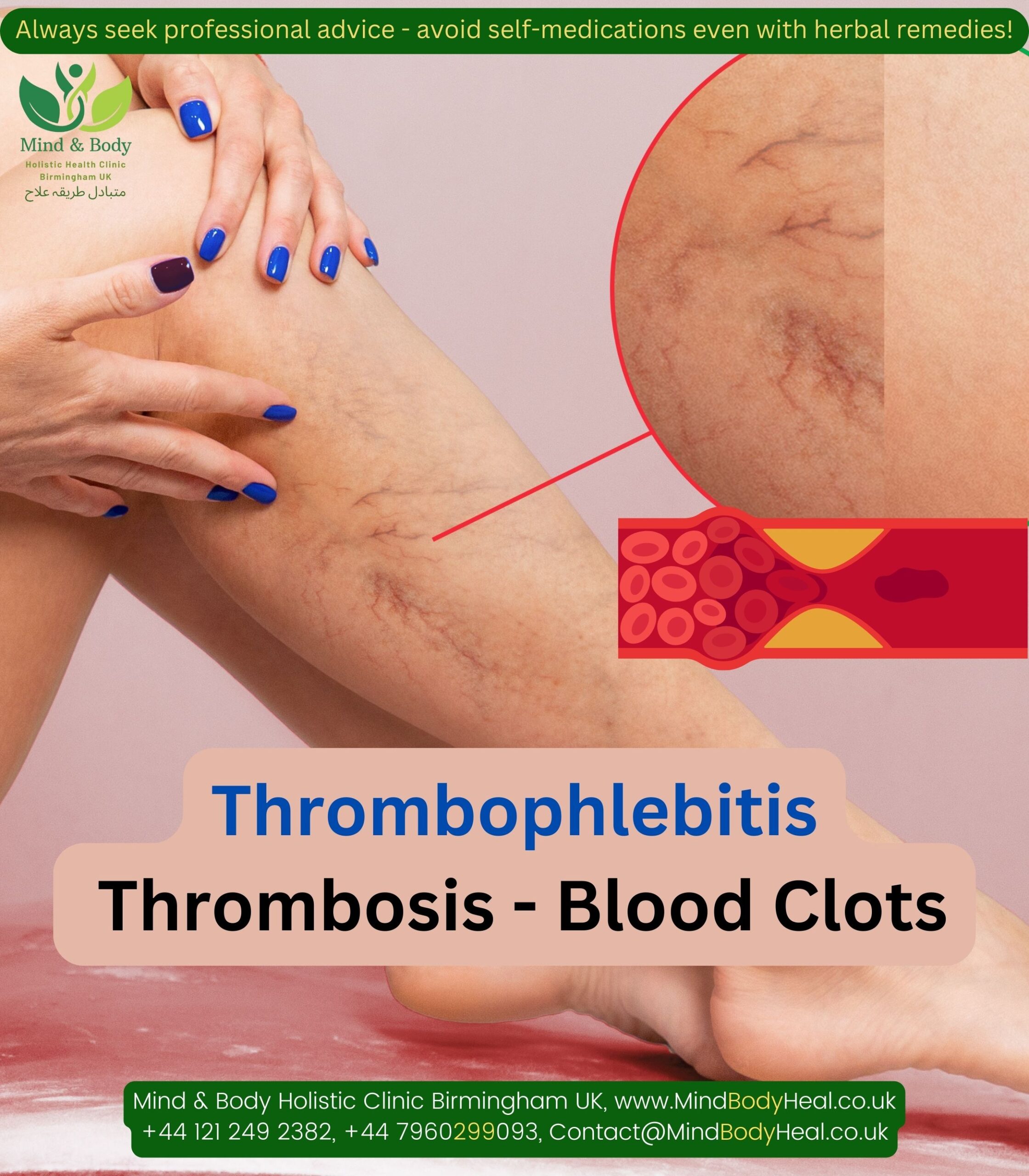
Thrombophlebitis is a condition that causes a blood clot to form and block one or more veins, often in the legs.
Clots in the blood stream can lead to dangerous complications like pulmonary embolism, coronary heart disease or stroke.
Blood clots stop you from losing too much blood after an injury, stop germs from getting into a wound and allow the wound to heal. However, sometimes blood clots form in the blood stream when there hasn’t been an external injury.
It’s possible for a blood clot (or thrombus) to form on the wall of a blood vessel or in the heart when blood, platelets, proteins and cells stick together. However, a blood clot stopping the flow of blood is a serious health issue that must be treated right away.
Typically, your body will naturally dissolve the blood clot when the injury has healed. Sometimes clots form on the inside of vessels when there is no external injury, or they don’t dissolve naturally.
If blood flows too slowly and starts to build up, large numbers of platelets may group together, stick to each other and form a blood clot. When blood clots form inside of your veins without a good reason, and don’t dissolve naturally, they urgent medical attention.
Luckily, blood clots are the most preventable types of blood conditions – you can decrease your chances of developing a blood clot with simple lifestyle changes. If you already have a blood clot, there are things you can do to limit the amount of time you are on blood thinners and other conventional forms of treatment.
Common Blood Clot Symptoms
Blood clot symptoms vary depending on where the clot is located.
Heart — heaviness or pain in the chest, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, light-headedness, and discomfort in other areas of the upper body
Brain — weakness of the face, arms or legs, vision problems, difficulty speaking, sudden and severe headache and dizziness
Lung — sharp chest pain, shortness of breath, racing heart, fever, sweating and coughing up blood
Arm or Leg — sudden or gradual pain, swelling, tenderness and warmth
Abdomen — intense abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhoea.
Types of Blood Clots
Blood clots can occur in your veins or arteries. Both are vessels that help transport blood throughout the body, but they function differently.
Veins are vessels that carry oxygen-depleted blood away from the body’s organs and back to the heart. When an abnormal blood clot forms in a vein, it may restrict the return of blood to the heart, causing pain and swelling as blood gathers behind the clot.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a clot or thrombus in a major, or deep veins of the body.
It may be primary, non-inflammatory process or a secondary reaction to local or distant inflammatory process.
Most deep vein blood clots occur in the lower leg or thigh. But they can also occur in other parts of the body, like the arms or pelvis.
When a blood clot in a deep vein breaks off and travels through the bloodstream, the loose clot is called an embolus. An embolus can travel through the heart to an artery in the lungs where it becomes wedged and blocks blood flow.
This is an extremely dangerous, life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism and require immediate attention.
Possible causes of thrombosis
- Genetics or family history
- Old age – Being older than 60
- Prolonged bed rest or lack of physical activity
- History of previous episodes of thrombophlebitis
- Have had a stroke
- Obesity or being overweight
- Varicose veins
- Pregnancy or Post delivery
- Use of oral contraceptive
- Use of a hormone replacement therapy, which can make your blood more likely to clot
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- History of certain medical conditions such as Myocardial infarction, Congestive heart failure, Cancer of pancreas or lungs
- Some cancers and their medications increase substances in the blood that cause the blood to clot.
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Hip fracture
- Homocystinemia
- Surgery of abdomen and pelvis
- IBD’s – Inflammatory bowel disease e.g., Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Thrombocythemia (increased number of platelets in blood)
- Polycythaemia vera (increased number of red cell in blood)
- Myelofibrosis (fibrosis of the bone marrow)
- Coagulation disorders – deficiency of anticoagulants like Antithrombin III, Proteins C and S, Factor II or V leiden
- A pacemaker or have a thin, flexible tube (catheter) in a vein, for treatment of a medical condition, which may irritate the blood vessel wall and decrease blood flow.
Superficial thrombophlebitis signs & symptoms include:
- Warmth and pain in the affected area
- Redness and swelling
- Hard cord just under the surface of the skin that’s tender to touch.
While deep vein thrombosis signs and symptoms include:
- Swelling
- Pain in calf muscle and occasionally in ankle
- Sensation of tightness in the calf
- Deep calf tenderness
- Occasional tenderness in the region of groin
- Feeling of warmth in the affected leg
- Fullness of superficial veins
- Rise in temperature of the local area
- Local oedema (swelling)
- Cyanosis or blue discoloration that is change in skin color on the leg — such as red or purple, depending on the color of your skin
Typical signs of pulmonary embolism include.
- Sudden breathing difficulties
- Coughing
- Coughing up blood
- Chest pain
Arterial Blood Clots. Clotting that occurs in the arteries is different than when it occurs in the veins. Arteries are muscular vessels that carry oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body. Clotting in the arteries is usually associated with the hardening of the arteries, called atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis occurs when plaque narrows the inside of the vessel. Plaque is made of cholesterol, fatty substances, cellular waste products, calcium and fibrin, a clotting material in the blood. When the passage in the artery begins to narrow, the strong arterial muscles continue to force blood through the opening with a lot of pressure. This can cause the plaque to rupture.
The molecules that are released in the rupture can cause the body to react by forming an unnecessary clot in the artery. At this point, your tissues and organs no longer get enough blood or they might not get any blood at all. Because this kind of blood clot usually develops in the coronary arteries or inside the heart, it can cause a heart attack or stroke. In fact, atherosclerosis is the primary cause of heart disease and stroke.
Venous Blood Clots – In superficial thrombophlebitis, the vein is near the surface of the skin. In deep vein thrombosis or DVT, the vein is deep within a muscle. Blood clots that form in the deep veins of the legs if blood flow is restricted, and it slows down. This may happen when you are.
- Immobile for long periods such as after surgery
- During a long trip in an airplane or car
- Stay in bed for an extended time.
Factors that can increase your risk of developing venous blood clots include
- Surgeries or trauma
- A family history of blood clots
- Age (over 60 years old)
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Oral contraceptives
- Cancer or coagulation disorders
Causes and risk factors for arterial clots include;
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
There is a dramatic increase in the risk of both arterial and venous blood clots with age. This may be due to;
- Vessel wall damage
- Decreased regular exercise
- Increasing immobility
- Increasing systemic activation of blood coagulation
DO’S & DONT’S – Prevention
- Do gentle exercise of extremities while in bed
- Elevate the legs by keeping a pillow etc. under the legs during sleep to reduce the oedema
- Take a walk. If you’re flying or riding a long-journey such as in a train, bus or in your care, walk up and move around. .
- Move your legs regularly.
- Flex your ankles or carefully press your feet against the floor or footrest in front of you at least 10 times each hour.
- Drink plenty of water or other non-alcoholic fluids to avoid dehydration.
FREE Shipping included – Usually dispatched within 1 – 2 working days!
Are you concerned about your health or managing a recurring or chronic condition?
Our website provides informed guidance and initial supportive care for individuals who are finding it difficult to access their doctors or who have not experienced desired improvement with conventional options.
We help individuals explore a range of natural and holistic healing approaches to encourage balance and long-term wellness that may complement your healing journey.
We offer a ready-to-use complementary remedies kit designed to ease discomfort and support well-being, with clear instructions for each item.
The kit includes a personalised selection of remedies based on your signs, symptoms, and likely causative factors.
It may combine homeopathic medicines, herbal or daily supplements, a tailored diet plan, lifestyle guidance, practical tips, and topical applications where needed. It’s suitable if you value the healing potential of natural, holistic remedies.
Complementary remedies work best alongside standard medical treatments and can usually be taken safely with your regular medications.
Our homeopathic remedies follow Dr. Hahnemann’s traditional dilution and succussion methods and are prepared by a qualified naturopathic practitioner, supported by research, clinical experience, and observed outcomes in similar cases. Treatment duration can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on severity and chronicity. Outcomes vary with individual factors and case complexity.
If you prefer lactose pills instead of sucrose globules, let us know. Please also provide the patient’s age so we can supply appropriately sized pills. You can simply send this via WhatsApp at 07960 299 093.
These remedies may contain trace amounts of natural plant, mineral, or animal substances, preserved in medical-grade alcohol. Inform us of any allergies or dietary restrictions before purchase.
You may contact us before starting or book a detailed consultation (in person or via teleconsultation) with one of our experienced naturopath for your detailed assessment or personalized guidance.
Natural remedies can affect the body and may not suit everyone. At the start of treatment, some patients—especially with mental health or skin issues—may experience a temporary increase in symptoms. This may represent medicinal aggravation, indicating the body is responding, though symptoms may not be connected and simply coincidental. If they persist, contact us for support.
Why some patients choose natural, complementary or holistic remedies:
• Symptomatic relief and improved well-being
• Gentle options with fewer side effects
• Whole-person focus, addressing physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors
• Root-cause and preventive emphasis
• Encouragement of active self-care
• Support alongside conventional treatment
• Personalised and accessible care
Precautions:
• Inform your healthcare provider about any complementary therapies
• Some herbs or supplements may interact with conventional medications
• Do not replace conventional treatment for serious, chronic, or terminal conditions
These complementary remedy kits are provided for your own discretion and personal responsibility. Use them mindfully and avoid self-medicating in sensitive situations.
If you are looking for a specific remedy / kit not listed on our site or a customized formulation, contact us—our range is extensive and can be tailored to your physical and mental symptoms and causative factors.
Disclaimer:
Natural remedies—including homeopathic remedies, herbal supplements, and aromatherapy products—are generally safe for most people, including children and older adults. Still, consult your GP or healthcare provider before use, especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or managing chronic or serious conditions.
- Our remedies support general wellness and are not a substitute for medical advice.
- Review product details and make informed decisions before purchasing, particularly for ongoing or serious concerns.
- We provide general guidance only; detailed personalised consultations are not available through this platform.
- These remedies are intended for individuals able to follow instructions independently.
- Our support focuses on product use and general information; repeated or highly detailed personal queries may not receive individual responses.
- If you need frequent reassurance or highly tailored advice, please consult a qualified naturopath or healthcare provider before purchasing.
Due to strict UK regulations on the sale of medicinal products, we cannot give specific advice, without a face-to-face consultation.